Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation is a possible treatment method for more than 70 malignant and non-malignant diseases, and for some haematological diseases transplantation is the most important therapeutic and also the only option for a cure. The modern method of treatment with KMC achieves a success rate of more than 90% under optimal conditions (http://www.ztm.si). For such success, sufficient antigenic (HLA) compatibility between donor and recipient must be ensured. For this reason, Slovenia has been included in the global register of the World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA), in which voluntary donors who are HLA typed are registered. In the event of a match, procedures for collection and transplantation are carried out.
In some cases, it is possible to use the patient’s own stem cells for treatment, which is known as autologous donation. More often it is a donation based on sufficient tissue compatibility between relatives. According to Slovenian law, donation and transplantation can also take place between unrelated persons, whereby the principle of anonymity must be maintained. Donation from another donor is an allogeneic donation, for which we first search for a donor in Slovenia and then abroad.
Slovenia established a registry for unrelated donors, Slovenia Donor, in 1991 and became a full member of the World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA) registry the following year.
Cornea
Cornea transplantation is one of the most frequent and most successful tissue transplantations in Slovenia and in the world. This medical treatment is often the only method that can improve sight after a disease or injury. In Slovenia, corneas are procured from deceased donors after a cardiovascular death or a brain death. The removal of corneas is possible following consent given by the deceased person during lifetime or if their close relatives do not object. In addition to the consent obtained, a detailed assessment of the suitability of the cornea for transplantation by the physician responsible for the recipient is required.
Corneas are transplanted in two transplantation centres: the Department of Ophthalmology in the Ljubljana UMC and the Department of Ophthalmology in the Maribor UMC.
Other Tissues and Cells
Artificial insemination with biomedical assistance and reproductive cells
Four centres are registered in Slovenia for the activity of artificial insemination with biomedical assistance for couples; namely, the Ljubljana AIBA Centre, the Maribor AIBA Centre, the Postojna AIBA Centre, and the Dravlje Health Centre. This is the most comprehensive area in terms of the number of procedures conducted.
Procuring and storing umbilical cord blood and the umbilical cord
In Slovenia, haematopoietic stem cells from umbilical cord blood and umbilical cord as well as from other tissues (e.g. milk teeth) are procured. One public tissue bank, the Blood Transfusion Centre of Slovenia (hereinafter: BTCS), and three privately-owned institutions (Izvorna celica, Biobanka and FH-S) have a licence for this activity. Public banks only allow allogeneic transplants, while private banks allow autologous transplants. The public umbilical cord blood bank within the BTCS stopped accepting samples of umbilical cord blood on 1 January 2015 as a sufficient number of samples had been collected and stored to meet Slovenia’s needs.
Single European tissue and cell code
Directive 2006/86/EC requires tissue establishments to use a single European code for the clinical use of tissues and cells within the EU. A single European code is a unique identifier for each tissue or cell. It consists of two parts: the donation identification number, which indicates the origin of the tissues or cells, and the product identification sequence, which classifies the type of tissues or cells. Details can be found in Annex VII:
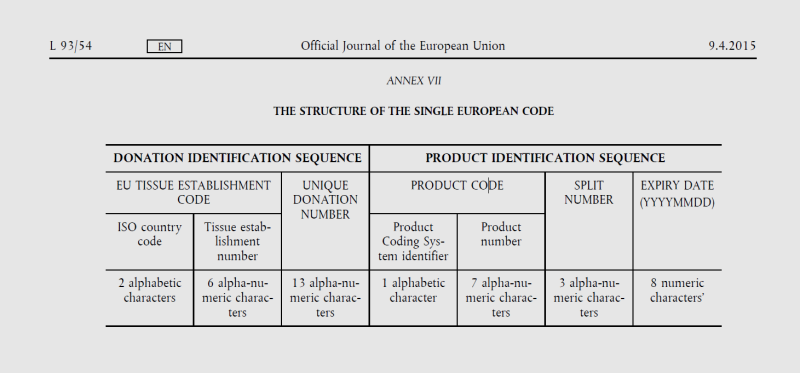
Further information about the European Tissue Code can be found under the following link:
EU Coding Platform
Interpretation of the European Tissue Code
Differences between the European Tissue Code and the Slovenian (national) Tissue Code:
- the Slovenian national tissue code has SI instead of E in the identifier of the product coding system;
- the coding of tissues is done according to a different coding system, as the Slovenian tissue code has eight alphanumeric character values (numbers) in the tissue number (product number), while the European tissue code has seven alphanumeric values (numbers).
Example:
SI 010185 0000000000723 E 0000053 001 20220129
SI 010185 0000000000723 SI 01040100 001 20220129
Tissue and Cell Institutions
In Slovenia, 27 institutions are involved in the activity of procuring and using tissues and cells on the national level. Fifteen hospitals are included in the programme and, within these, 40 clinical departments. In terms of their status, 18 tissue and cell institutions are public and 9 privately-owned. Private institutions hold a permit exclusively for the autologous procurement of tissues and cells.
Slovenija-transplant and Agency for Medicinal Products and Medical Devices of the Republic of Slovenia (JAZMP) ensure that the system functions transparently and promptly identify and discuss any deviations that could affect the quality and safety of the tissues and cells of donors, recipients as well as the staff involved in the processes.
To obtain a permit, every institution must comply with strict expert and legal terms and provisions. All institutions have set up a quality assurance system where all the procedures for ensuring the conditions for tissue and cell quality and recipient safety are defined. They are regularly supervised by JAZMP, whereas Slovenija-transplant also performs verification of the data reported.


